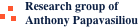Balancing and Reserves
Context: The increasing integration of renewable resources in power systems increases the needs of the system for flexibility in the form of reserve resources that can rapidly balance fluctuations in system supply. Meanwhile, renewable resources also depress energy prices due to their low marginal cost. This creates...
View Project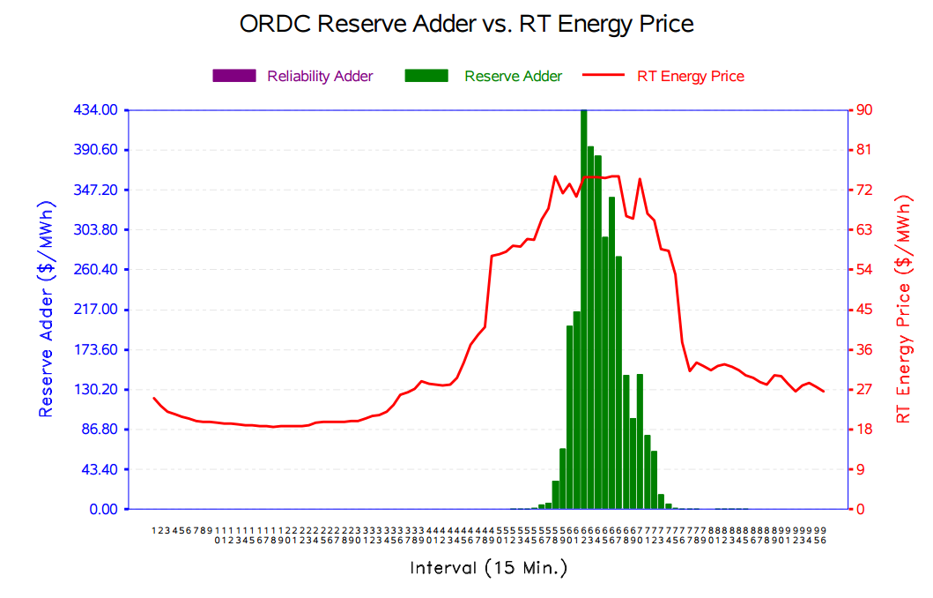
Congestion Management
Context: In a regime of increasing uncertainty and variability due to the growing integration of renewable energy sources, the patterns of flows along electricity networks change rapidly and unpredictably. This requires network operators to adapt the dispatch of conventional resources so as to respect the physical l...
View Project
Optimization under Uncertainty
Context: Renewable resources such as wind and solar power are characterized by an inherently unpredictable supply. Much of this uncertainty is revealed close to real time, while planning decisions which related to the commitment of adequate generating resources for ensuring reliable system operation must be reached ...
View Project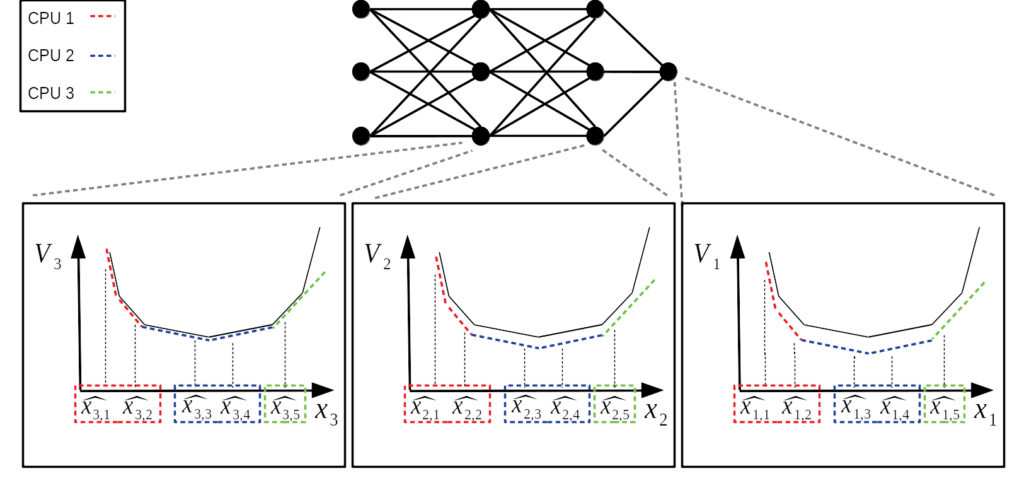
Transmission-Distribution Coordination
Context: A major challenge of the ongoing energy transition relates to the fact that distribution networks, with increasing amounts of distributed renewable resources, are no longer only consuming power generated by the transmission network, but also producing power through distributed renewable resources (such as s...
View Project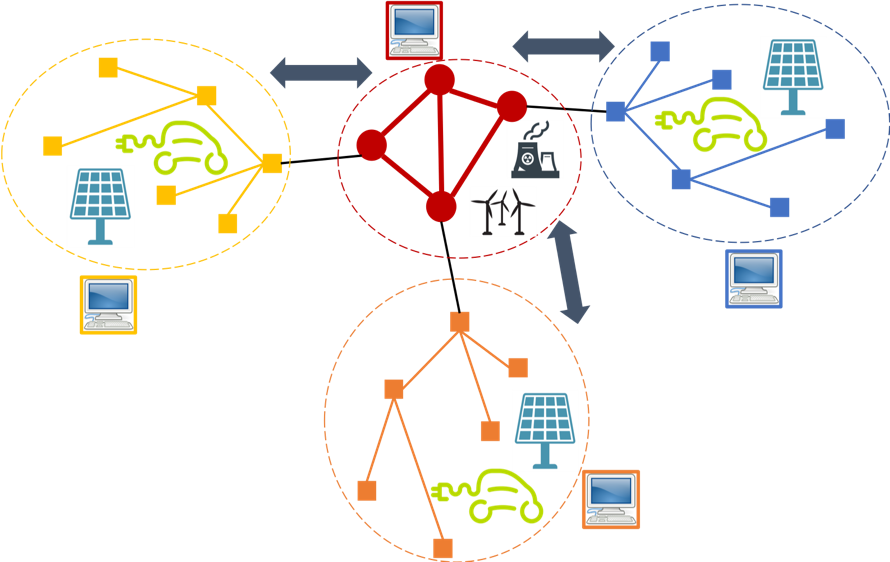
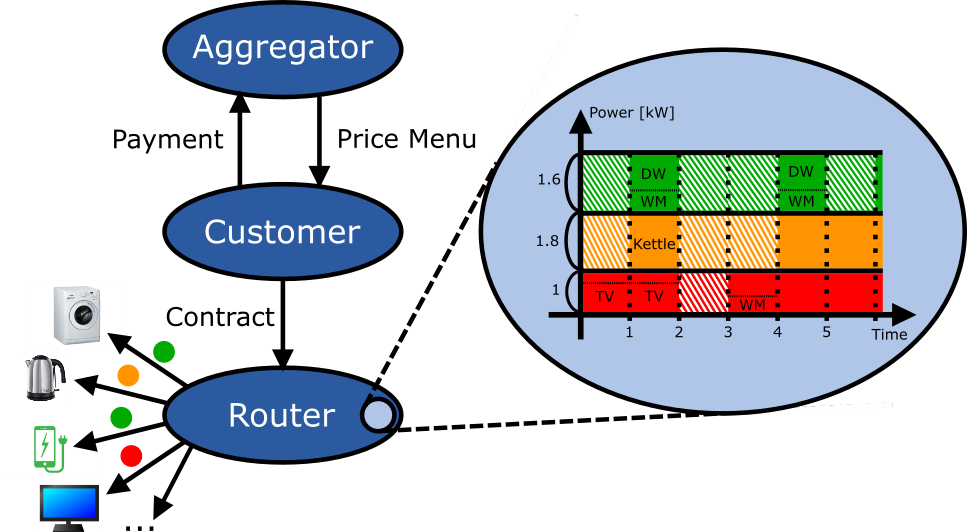
Demand Response
Context: A significant portion of the electricity that we consume can be shifted in time with a relatively minor impact on our comfort. Consider, for example, dish washers, laundry, dryers, or in the future electric vehicle charging: some of the most energy-intensive devices in our homes also happen to be deferrable...
View Project